Astro 122: Astronomy of Stars and Galaxies



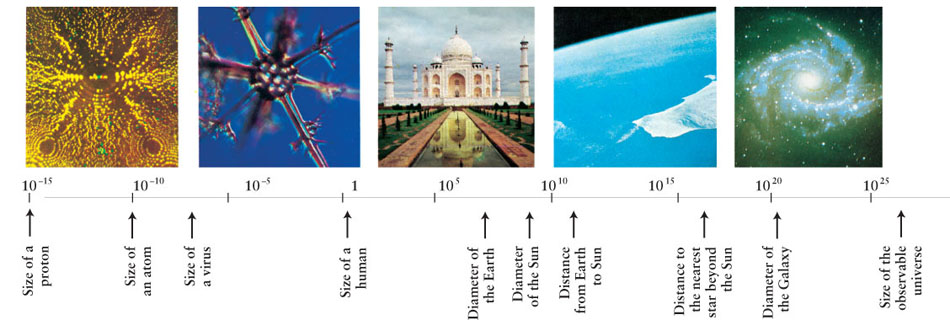
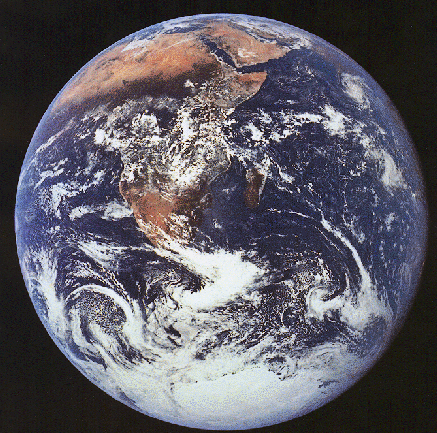 |
The Earth
Light could travel around the Earth's equator about 8 times in one second. |
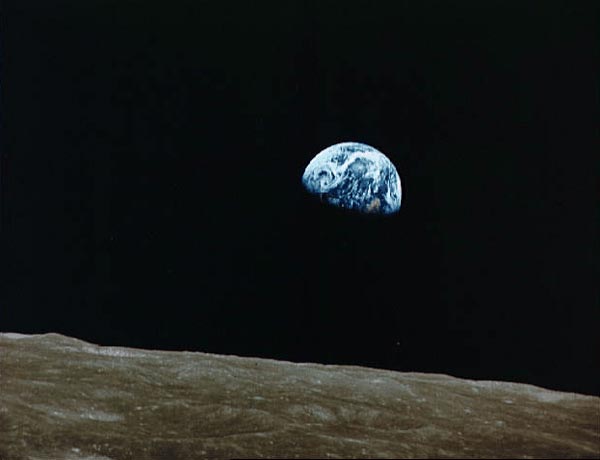
The Earth seen from the Moon
|
 |
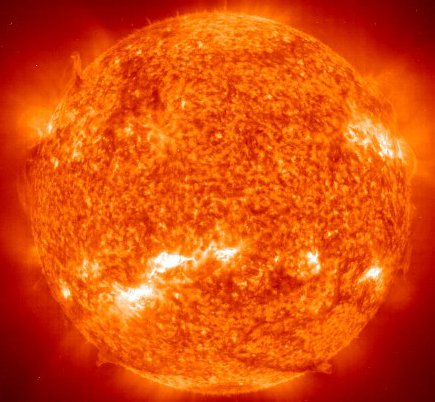
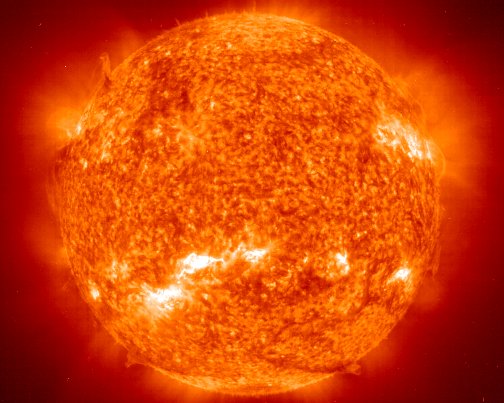
The Sun
|
|
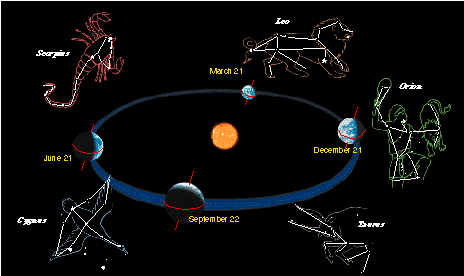
The Earth's Orbit Around the Sun
|
 |
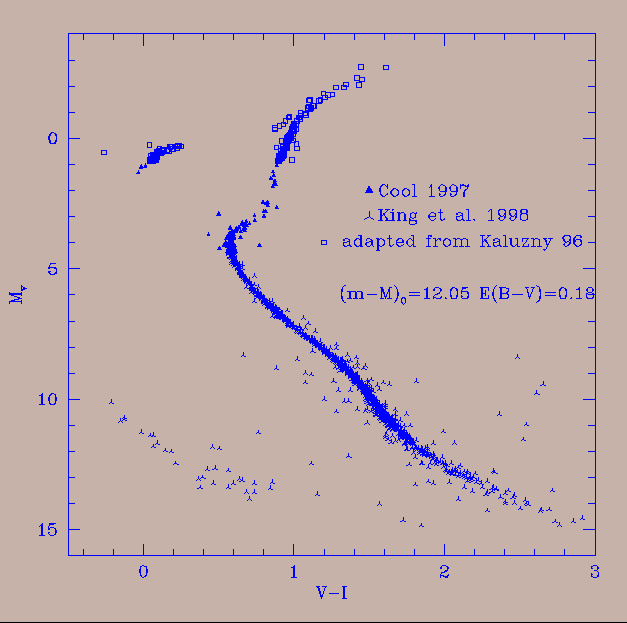
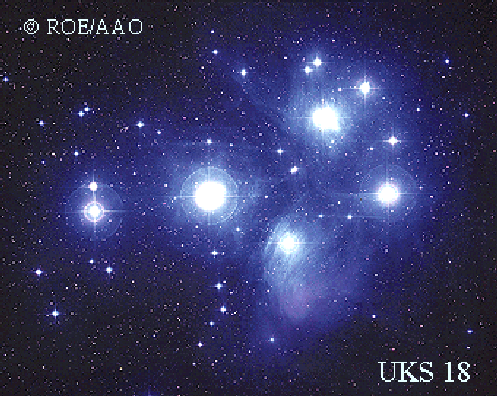
The Pleiades Star Cluster
|
 |
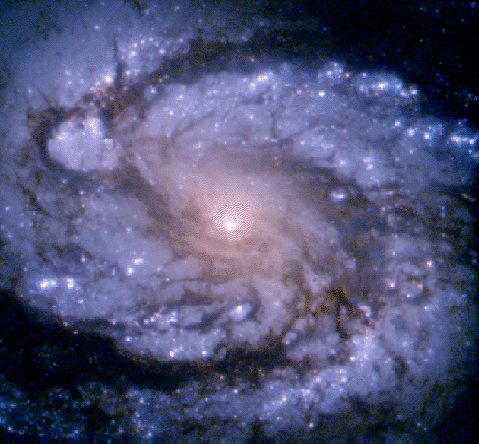
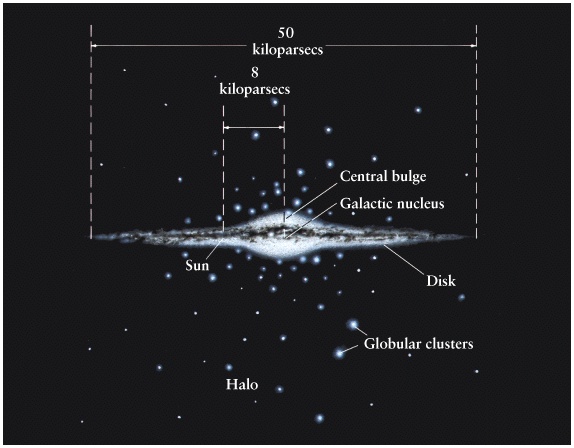
The Milky Way Galaxy
|
 |
The Andromeda Galaxy
|
 |
The Virgo Cluster of Galaxies
|
 |
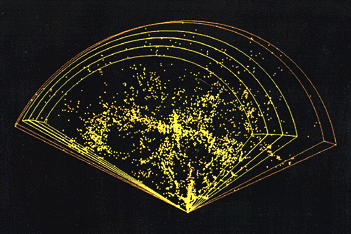
Superclusters
|
 |
The Hubble Deep Field
|
 |